
What is Progressive Wage Model?
The Progressive Wage Model (PWM) helps to increase the wages of workers by upgrading skills and improving productivity. It is implemented via government levers in the cleaning, security, and landscape sectors.
The PWM covers Singapore citizens and Singapore permanent residents (PRs) in the cleaning and security sectors, as well as landscape companies on NParks’ Landscape Company Register.
Employers are encouraged to use these principles of progressive wages for foreign cleaners, security officers, and landscape maintenance employees.
Who it covers
The progressive wage model requirements cover Singapore citizens and permanent residents who are:
- Full-time or part-time employees in retail job roles on a contract of services, and
- Employed by firms that hire foreign workers, regardless of whether the firm is classified under the Retail Trade Singapore Standard Industrial Classification (SSIC) or another SSIC.
The retail PWM will cover the following retail job roles:
Cashier:
Responsibilities:
- Assist customers in the in-store checkout process
- Attend to customers’ queries at the cashier counter
- Implement current promotional events during the checkout process
Retail Assistant
Responsibilities:
- Sell and explain the functions and qualities of products
- Assist customers by pointing out or demonstrating the features and merits of products
- Manage and maintain store display standards and arrangement of products
- Stock-take and replenish stock according to the company’s Standard Operating Procedures
Senior Cashier
Responsibilities:
- Mentor and guide the work execution of other cashiers
- Plan resources to support smooth operation in the checkout department
- Conduct on-job-training for new cashiers
- Perform the responsibilities of a cashier
Senior Retail Assistant
Responsibilities:
- Mentor and guide the work execution of other retail assistants
- Handle customer inquiries on promotions and lead customers to products
- Conduct on-job-training for new retail assistants
- Perform the responsibilities of a retail assistant
Assistant Retail Supervisor
Responsibilities:
- Assist the retail supervisor to oversee the daily store operations
- Achieve store’s sales target and maximize profitability
- Prepare monthly roster of the sales team
- Supervise, coach, counsel, and coordinate the activities of retail assistants, cashiers, and third-party staff
Retail Supervisor
Responsibilities:
- Ensure operational demands are catered for
- Possess strong product and customer service knowledge
- Conduct training for roles in the store
- Perform the responsibilities of an assistant retail supervisor
Retail Manager
Responsibilities:
- Oversee end-to-end operations
- Ensure Standard Operating Procedures are followed
- Make decisions on customers’ issues and service recovery
- Drive, analyze, improve, and achieve sales and service performance
Wage requirements
The retail PWM is a five-level career progression model. It features:
- Specific training requirements that tap on the Skills Framework for Retail. This ensures that retail workers are equipped with the skills needed to carry out their job functions.
- Progressive wages are set at each level to ensure that retail workers are paid wages that are commensurate with their skills and productivity.
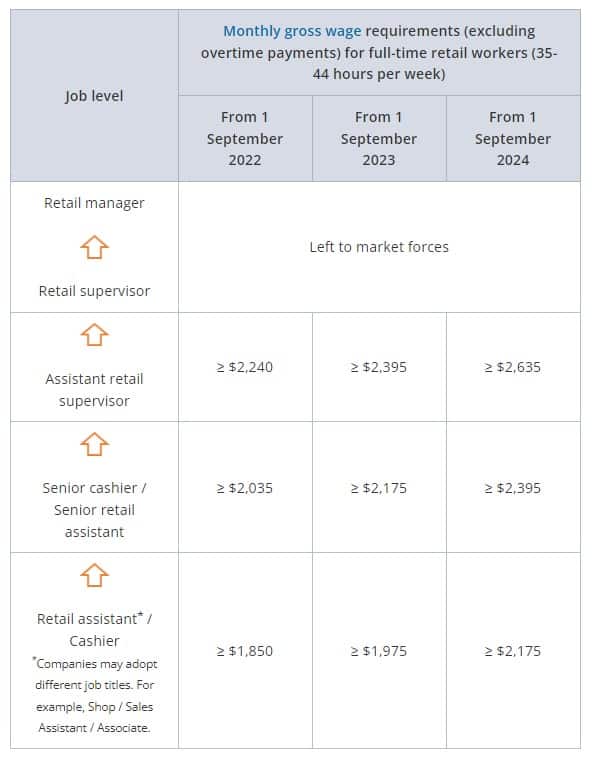
The wage requirements recommended in the TCR’s report will take effect from 1 September 2022.
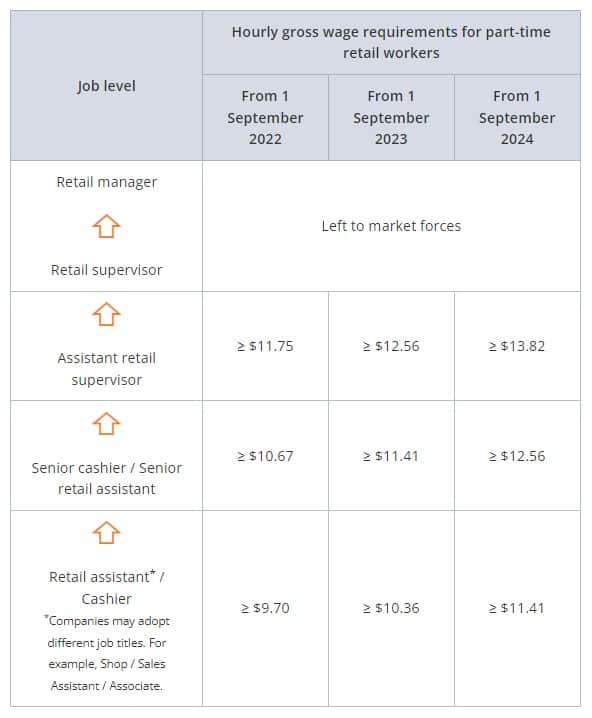
Wage requirements for part-time workers are pro-rated on a 44-hours basis.
The TCR will undertake a review of the wage schedule in 2024.
Full-time Retail Workers
Part-time Retail Workers
Please note:
Total monthly gross wage (for full-time work of 35-44 hours per week) refers to the sum of:
- basic wage,
- allowances, e.g. travel, food, housing, and
- productivity incentive payments.
It excludes:
- bonuses, e.g. Annual Wage Supplement,
- stock options,
- reimbursement of special expenses incurred in the course of employment,
- payments-in-kind, and
- employer CPF contributions.
Additional PWM gross wage requirements for overtime
For full-time workers who work more than 44 hours a week and are covered by the Employment Act’s Part 4, employers would need to adhere to additional PWM gross wage requirements for overtime. Overtime pay can be part of the gross wage used to meet these additional requirements.
In addition to meeting the PWM requirements for overtime, employers need to ensure that they adhere to the Employment Act’s Part 4 requirements for overtime, where the overtime rate of pay must be at least 1.5 times the basic rate of pay.
Averaging of gross wages
Given that the retail sector sees seasonal fluctuations in sales revenue throughout the year, the TCR has agreed to the averaging of the wage requirements for retail employees covered by the retail PWM over a 3-month period.
To qualify and meet retail PWM requirements for each retail employee in a specific month, employers must fulfill either one of these conditions:
- Gross wage paid for a month is equal to or higher than that month’s wage requirements (inclusive of OT pay, if any), OR
- The past 3 months’ average gross wage is equal to or higher than the average of the past 3 month’s wage requirements (inclusive of OT pay, if any).
For more details, refer to the worked examples on the averaging arrangement in Annex D of the TCR’s report.
Training requirements
Employers must ensure that their Singapore citizens and PR retail workers meet the retail PWM training requirements of attending at least 1 Workforce Skills Qualification (WSQ) training module out of the list of approved courses.
Alternatively, if employers have in-house WSQ training modules that have the prefix “RET” in the accompanying Technical Skills & Competencies (TSC) code, these training modules can be used to meet the training requirement as well.
Through proper training, retail workers will be able to increase their productivity and offer good retail experiences to customers.
Refer to Annex C of the TCR’s report for more details.

