What is Progressive Wage Model?
The Progressive Wage Model (PWM) helps to increase the wages of workers by upgrading skills and improving productivity. It is implemented via government levers in the cleaning, security, and landscape sectors.
The Progressive Wage Model (PWM) for food services workers was developed by the Tripartite Cluster for Food Services Industry (TCF).
From 1 March 2023, employers must meet the PWM requirements of attaining at least 2 Workforce Skills Qualification (WSQ) Statement of Attainment, out of the list of approved WSQ training modules in order to renew existing work passes or apply for new work passes. in order to renew existing work passes or apply for new work passes.
Who it covers
The PWM requirements cover Singapore citizens and permanent residents who are:
- Full-time or part-time food services employees on a contract of service, working in a premise that has a Singapore Food Agency (SFA) Food Retail or Food Processing (Central Kitchen) licence, and
- Employed by firms that hire foreign workers on mainstream work passes (i.e. Work Permit, S Pass, Employment Pass), regardless of whether the firm is classified under the Food and Beverage Service Activities Singapore Standard Industrial Classification (SSIC) or another SSIC.
Find out more on the coverage of food services job roles and the description of duties and responsibilities.
The Food Services PWM has 2 sectors: Category A and Category B
Coursemology provides a comprehensive suite of modules that helps companies meet the mandatory training requirements.
| Category A Quick-Service (QS) food establishments, including fast-food outlets, food courts, food kiosks, and eating houses where customers self-collect food or drink orders from food service counters Supermarkets with ready-to-eat food station. | Recommended Modules |
| Food/Drink Stall Assistant Responsibilities: -Prepare or serve simple food/drink items from counters or steam tables in food stalls -Take customer orders and communicate orders to the kitchen -Collect payment from customers and perform cashiering duties Examples of jobs covered: -Food court stall assistant -Coffeeshop stall assistant | -WSQ Food Hygiene Course Level 1 -WSQ Workplace Safety and Health for Food and Beverage Operations Level 2 -Prepare for Service |
| Food Service Counter Assistant Responsibilities: -Prepare or serve simple food/drink items from counters or steam tables in food shops -Take customer orders and communicate orders to the kitchen -Collect payment from customers and perform cashiering duties -Handle commercial or industrial-grade equipment, e.g. coffee machines, deep fryers, griddles -Manage online orders, e.g. via digital platforms Examples of jobs covered: -Fast-food service crew -Bubble tea shop service crew -Salad counter server -Roast grill counter attendant | -WSQ Food Hygiene Course Level 1 -WSQ Workplace Safety and Health for Food and Beverage Operations Level 2 -Prepare for Service |
| Kitchen Assistant (QS) Responsibilities: -Handle basic food preparation -Prepare ingredients for cooking according to the establishment’s standard recipes and operating procedures -Portion, assemble, or package menu dishes and other food items -Process new inventory items and inventory checking -Clean food preparation areas, kitchen stations, equipment, tables, cutlery, and crockery -Prepare food items for ready consumption -Provide counter service, where needed -Collect payment from customers and perform other cashiering duties -Package food/drinks for takeaways Examples of jobs covered: -Kitchen Assistant -Kitchen Crew -Bakery Assistant | -WSQ Food Hygiene Course Level 1 -WSQ Workplace Safety and Health for Food and Beverage Operations Level 2 |
| Cook (QS) Responsibilities: -Supports the preparation of menu dishes -Assemble ingredients or kitchen equipment prior to preparation of menu dishes, according to the establishment or senior cook’s requirements -Apply culinary techniques to prepare food according to the establishment’s standard recipes and operating procedures -Supervise kitchen assistants -Maintain cleanliness of kitchen stations and upkeep of cooking equipment -Prepare batches of food that are cooked to order, or kept warm until ordered and sold Examples of jobs covered: -Commis chef -Line cook -Pastry chef -Baker | -WSQ Food Hygiene Course Level 1 -WSQ Workplace Safety and Health for Food and Beverage Operations Level 2 |
| Senior Cook (QS) Responsibilities: -Direct and manage the preparation of menu dishes at one or more kitchen stations -Apply culinary techniques to prepare food according to the establishment’s standard recipes and operating procedures -Support the sous chef and head chef in the development of new menu dishes -May oversee one or more kitchen assistants, cooks or other kitchen staff Examples of jobs covered: -Chef de Partie -Station chef | -WSQ Food Hygiene Course Level 1 -WSQ Workplace Safety and Health for Food and Beverage Operations Level 2 |
| Category B -Full-Service (FS) food establishments, which are establishments that have wait staff such as waiters or banquet servers and are not under Category A -Caterers -Central kitchens | Recommended Modules |
| Kitchen Assistant (FS) Responsibilities: -Handle basic food preparation -Prepare ingredients for cooking according to the establishment’s standard recipes and operating procedures -Portion, assemble, or package menu dishes and other food items -Process new inventory items and inventory checking -Clean food preparation areas, kitchen stations, equipment, tables, cutlery, and crockery -Assist in cooking and plating menu dishes according to the kitchen manual, where applicable Examples of jobs covered: -Kitchen Assistant -Kitchen Crew -Bakery Assistant | -WSQ Food Hygiene Course Level 1 -WSQ Workplace Safety and Health for Food and Beverage Operations Level 2 |
| Cook (FS) Responsibilities: -Supports the preparation of menu dishes -Assemble ingredients or kitchen equipment prior to preparation of menu dishes, according to the establishment or senior cook’s requirements -Apply culinary techniques to prepare food according to the establishment’s standard recipes and operating procedures -Supervise kitchen assistants -Maintain cleanliness of kitchen stations and upkeep of cooking equipment -Follow the senior cook’s instructions for the preparation of menu items and meeting of other operational needs -Support compliance with food safety and sanitation requirements, in areas such as product rotation, temperature maintenance, storage procedures, and food handling techniques Examples of jobs covered: -Commis chef -Line cook -Pastry chef -Baker | -WSQ Food Hygiene Course Level 1 -WSQ Workplace Safety and Health for Food and Beverage Operations Level 2 |
| Senior Cook Responsibilities: -Direct and manage the preparation of menu dishes at one or more kitchen stations -Apply culinary techniques to prepare food according to the establishment’s standard recipes and operating procedures, where applicable -Support the sous chef and head chef in the development of new menu dishes -May oversee one or more kitchen assistants, cooks, or other kitchen staff Examples of jobs covered: -Chef de Partie -Station chef | -WSQ Food Hygiene Course Level 1 -WSQ Workplace Safety and Health for Food and Beverage Operations Level 2 |
| Waiter Responsibilities: -Attend directly to customers’ needs and supports customer-facing operations -Prepare tables for service, greet walk-in customers, and escort them to their tables -Respond to customer inquiries and take reservations over the telephone -Take customer orders and communicate orders to the kitchen – may be done manually -Serve food/drinks from the kitchen to customers -Collect payment from customers and perform other cashiering duties Examples of jobs covered: -Waiter -Banquet server | -WSQ Food Hygiene Course Level 1 -WSQ Workplace Safety and Health for Food and Beverage Operations Level 2 -Prepare for Service |
| Waiter Supervisor Responsibilities: -Support the manager by overseeing customer-facing operations -Coordinate, manage, or train waiters and other customer-facing employees -Supervise customer interactions and intervene where necessary -Ensure compliance with regulations, as well as the establishment’s own service protocols and standards -Scheduled working shifts of waiters and other customer-facing employees based on operational needs -Manage payroll and manpower budget for waiters and other customer-facing employees Examples of jobs covered: -Waiter supervisor | -WSQ Food Hygiene Course Level 1 -WSQ Workplace Safety and Health for Food and Beverage Operations Level 2 -Prepare for Service |
| Manager Responsibilities: -Bear overall responsibility for the profitability of the establishment -Oversee all of the establishment’s operations, i.e. both customer-facing and back-of-house activities, e.g. kitchen, inventory management Examples of jobs covered: -Restaurant manager -Outlet manager | -WSQ Food Safety and Hygiene Level 3 -People Development for Retails Sector. |
Wage requirements for progressive wage model for food services
The food services PWM is a three to four-level career progression model, depending on a career track. It features:
-Specific training requirements that tap on the Skills Framework for Food Services. This ensures that food service workers are equipped with the skills needed to carry out their job functions.
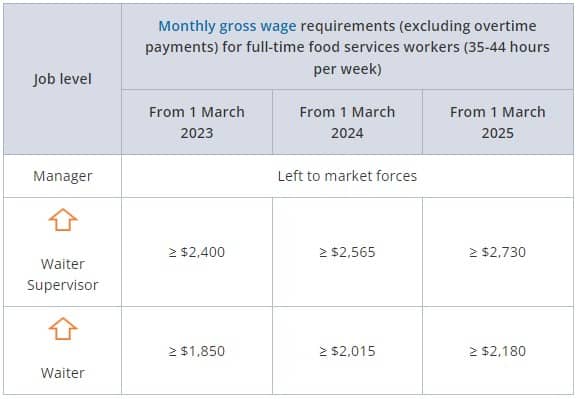
-Progressive wages are set at each level to ensure that food services workers are paid wages that are commensurate with their skills and productivity.The wage requirements recommended in the TCF’s report will take effect from 1 March 2023.
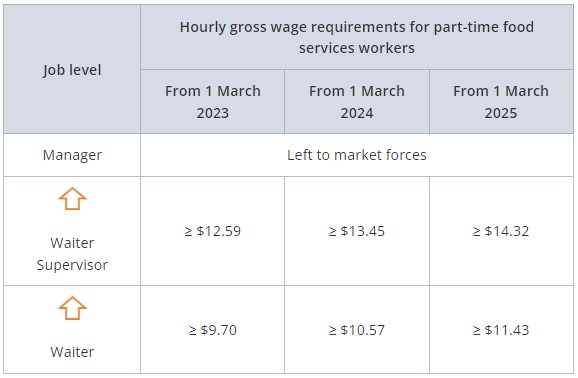
Wage requirements for part-time workers are pro-rated on a 44-hours basis.
The TCF will undertake a review of the wage schedule in 2025.
Category A
Full-time food service workers
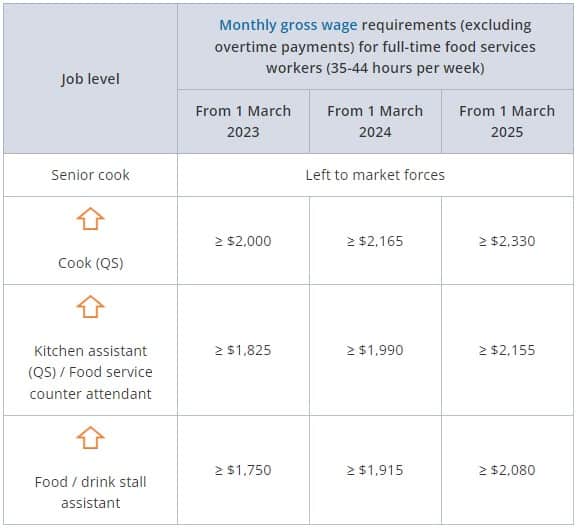
Part-time food service workers
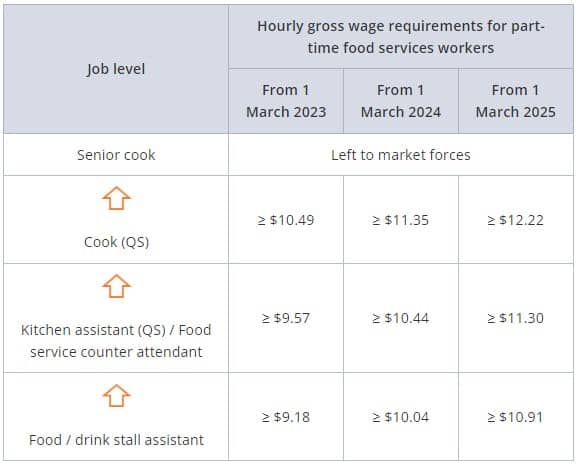
Category B
Kitchen Assistant/Cook/Senior Cook
Full-time food service workers
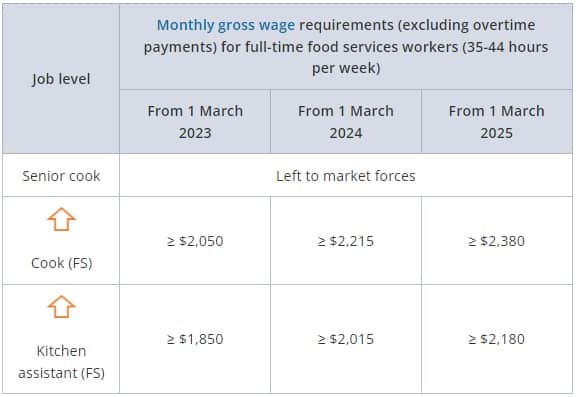
Part-time food service workers
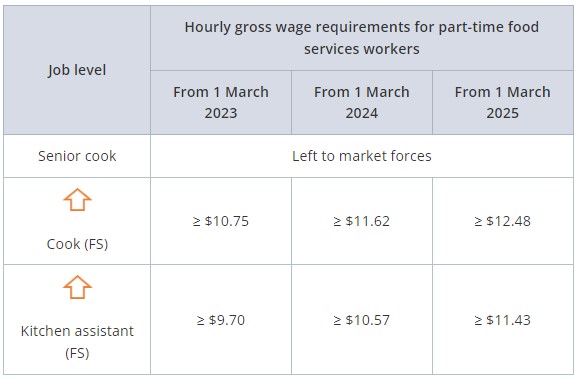
Waiter
Full-time food service workers
Part-time food service workers
Please note:
Total monthly gross wage (for full-time work of 35-44 hours per week) refers to the sum of:
- Basic wage
- Allowances, e.g. travel, food, and housing
- Productivity incentive payments
It excludes:
- Bonuses, e.g. Annual Wage Supplement
- Stock options
- Reimbursement of special expenses incurred in the course of employment
- Payments-in-kind
- Employer CPF contributions
Additional PWM gross wage requirements for overtime
For full-time workers who work more than 44 hours a week and are covered by the Employment Act’s Part 4, employers would need to adhere to additional PWM gross wage requirements for overtime.
In addition to meeting the PWM requirements for overtime, employers would need to adhere to the Employment Act’s Part 4 requirements for overtime, where the overtime rate of pay must be at least 1.5 times of the basic rate of pay.
Training requirements
Employers must ensure that their Singapore citizen and PR food services workers meet the food services PWM training requirements of attaining at least 2 Workforce Skills Qualification (WSQ) Statement of Attainment, out of the list of approved WSQ training modules.
Alternatively, if employers have in-house WSQ training modules that have the prefix “FSS” in the accompanying Technical Skills & Competencies (TSC) code, these training modules can be used to meet the training requirements as well.
For the job roles of senior cook and manager, training as per the list of approved WSQ training modules is encouraged but not mandatory. Employers have the flexibility to train employees in senior positions according to their own business needs.
Employers will be given a grace period to comply with the food services PWM training requirements:
- For new hires: six months from the new hire’s date of employment
- For existing employees: up till 29 February 2024 (one year from the food services PWM implementation on 1 March 2023)
Through proper training, food services workers will be able to increase their productivity, skillsets, and offer good food service experiences to customers.
Phased implementation of food services PWM
From the first six months from March 2023 to August 2023, MOM will give employers time to adjust and comply with the food services wage requirements.
Instead of enforcement, MOM will focus on educating employers on the food services PWM wage requirements. Those who do not comply with the requirements during this transitional period will not have their work pass privileges suspended.
Find out more at TCF’s report and recommendations on PWM for food services sector


